Constructing a Pallet Shed Utilizing Free Plans: A Guide to Economical Construction
The allure of a cost-effective and functional storage solution is undeniable. A pallet shed, constructed using reclaimed materials and readily available free plans, offers a compelling alternative to commercially-built structures. This comprehensive guide details the process of building a robust and aesthetically pleasing pallet shed, emphasizing practicality and minimizing expenses. While utilizing free plans necessitates a degree of DIY expertise, this guide aims to simplify the process for even moderately experienced builders.
I. Planning and Preparation: Laying the Foundation for Success
Before embarking on construction, meticulous planning is paramount. This stage encompasses several key aspects that directly influence the project's outcome and longevity.
A. Sourcing Materials: The Heart of Cost-Effectiveness
The cornerstone of a budget-friendly pallet shed lies in acquiring suitable pallets at minimal or no cost. Several avenues exist:
- Local Businesses: Contact nearby supermarkets, grocery stores, and distribution centers. Many are willing to relinquish used pallets rather than dispose of them.
- Construction Sites: Construction sites often have a surplus of pallets. Inquire politely about their disposal practices and potential availability.
- Online Classifieds: Websites and applications dedicated to classified advertisements often feature free or low-cost pallet listings.
- Recycling Centers: Some recycling centers may offer pallets for a small fee or even for free.
B. Selecting a Suitable Location: Considerations for Placement
The shed's location profoundly affects its functionality and longevity. Factors to consider include:
- Accessibility: Ensure easy access for loading and unloading items.
- Ground Conditions: Level, well-drained ground is essential for a stable foundation. Consider using gravel or concrete pavers for added stability, especially in softer soils.
- Sun Exposure and Weather Protection: Position the shed to minimize direct sunlight and exposure to prevailing winds and rain. Consider the orientation in relation to potential snow accumulation.
- Local Regulations: Check local building codes and zoning regulations concerning shed construction and placement.
C. Choosing the Right Free Plans: A Foundation for Success
Numerous free pallet shed plans are available online. Thoroughly review several options to select a design matching your needs and skillset. Consider the following criteria:
- Dimensions: Choose a size appropriate for your storage requirements and the available space.
- Complexity: Opt for a plan that aligns with your construction experience. Beginners should prioritize simpler designs.
- Material List: Ensure the plan provides a detailed list of materials needed, including lumber quantity and dimensions.
- Detailed Instructions: Select plans with clear, step-by-step instructions and accompanying diagrams.
II. Construction Process: Building Your Pallet Shed
The construction process follows a logical sequence, building upon the preparatory work. Careful attention to detail is critical for a structurally sound and aesthetically pleasing result.
A. Foundation Construction: Ensuring Stability
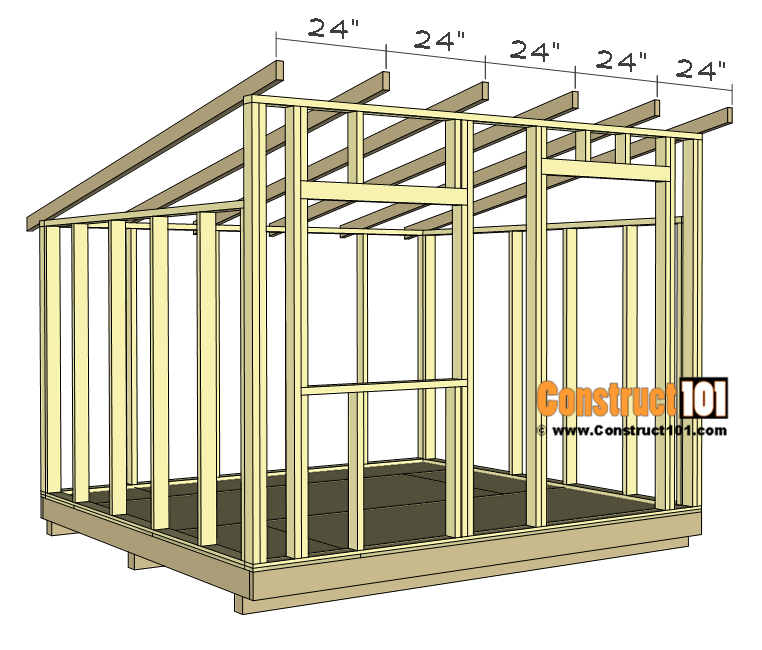
A solid foundation is essential for a durable shed. While a simple gravel base is sufficient for lighter sheds, consider a more robust concrete slab for heavier structures or unstable ground. Ensure the base is level and adequately sized for the shed's footprint. This stage may require specialized tools and materials depending on the chosen foundation type. Refer to your chosen plan for specific requirements.
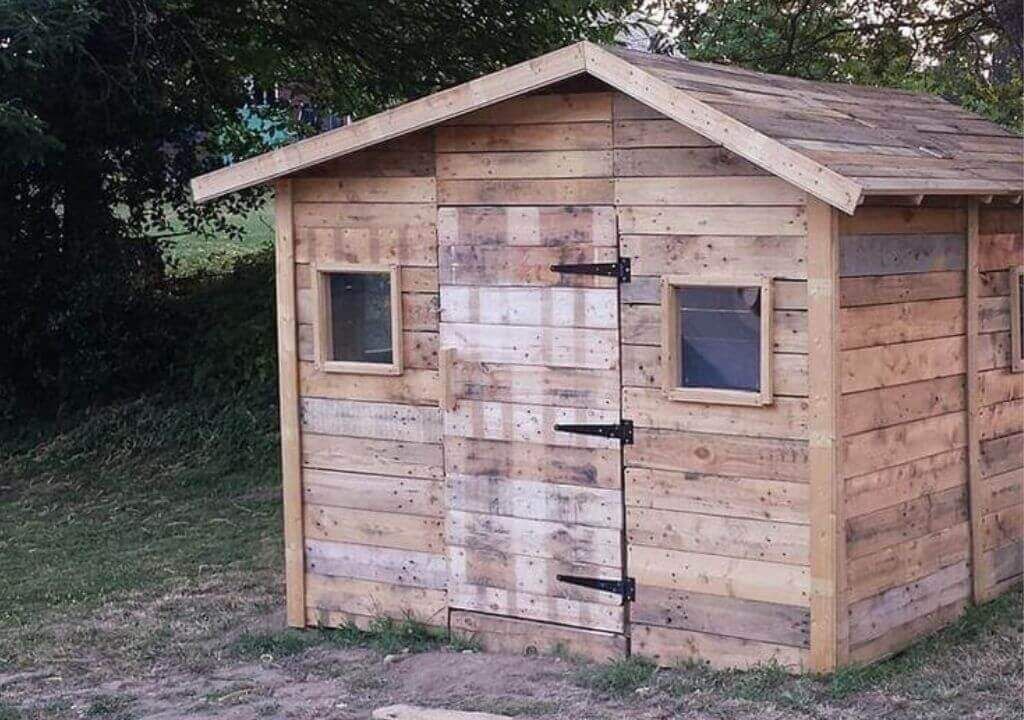
B. Pallet Preparation and Assembly: The Core Structure
Before assembling the pallets, inspect each one again for damage. Repair any significant damage using screws, wood glue, and wood filler. The assembly process typically involves connecting pallets using additional lumber and appropriate fasteners (screws, nails, or bolts). Pay close attention to the free plan's specifications for creating a structurally sound frame. Using a level ensures squareness and prevents warping. Pre-drilling holes before fastening reduces the risk of splitting the wood.
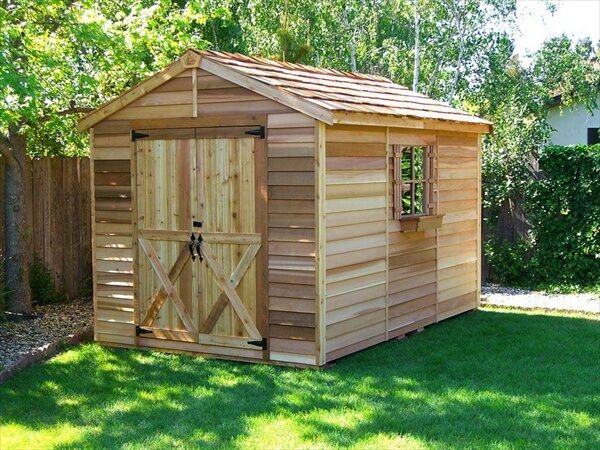
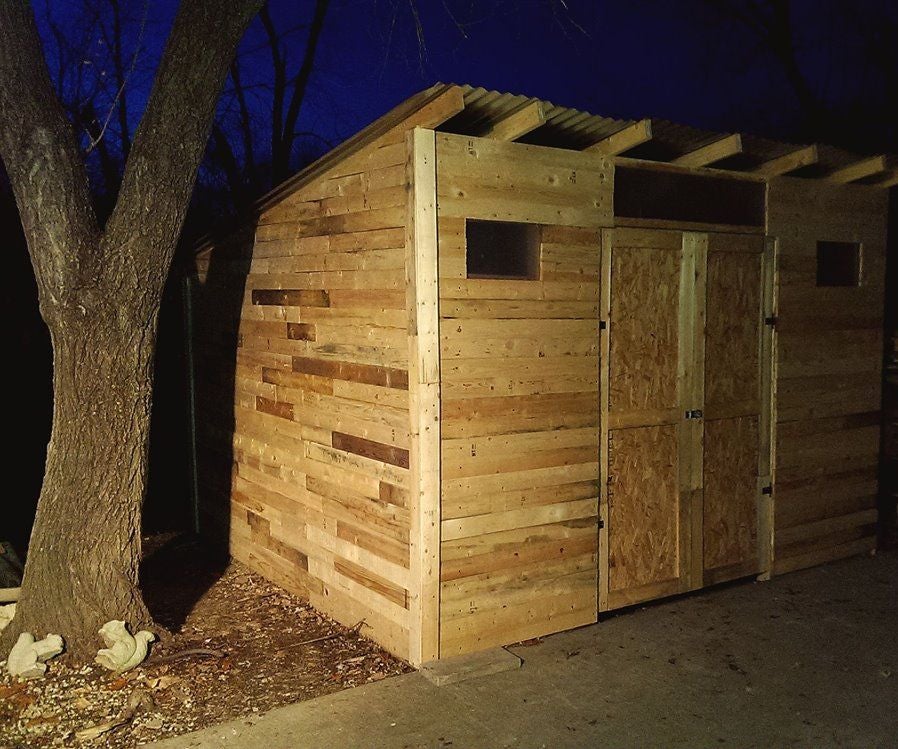
C. Roofing and Siding: Weather Protection and Aesthetics
The roofing system is crucial for protecting the shed's contents from the elements. The chosen roofing material (tar paper, corrugated metal, or recycled materials) will influence the construction method. Properly securing the roofing material is vital for preventing leaks and damage. Siding can be added for extra protection and improved aesthetics; pallet wood itself can be used for siding if creatively arranged. Consider using weather-resistant paint or sealant to enhance longevity.
D. Door and Window Installation: Access and Ventilation
Install the door and windows according to the free plan's specifications. Ensure proper sealing around the frames to prevent drafts and water infiltration. Use appropriate hinges and hardware for a secure and functional opening and closing mechanism. Consider adding latches or locks for security. Appropriate ventilation is important to prevent moisture buildup and potential damage to stored items.
III. Finishing Touches and Maintenance: Enhancing Longevity
The final stages involve refining the shed and implementing preventative maintenance to extend its lifespan.
A. Finishing and Aesthetics: Enhancing Visual Appeal
Consider adding finishing touches such as paint, stain, or sealant to protect the wood and enhance the shed's aesthetics. Select weather-resistant coatings designed for outdoor use. A fresh coat of paint can significantly improve the overall appearance and protect the wood from the elements.
B. Regular Maintenance: Ensuring Durability
Regular maintenance is crucial for prolonging the shed's life. This includes inspecting for damage, repairing any cracks or loose boards, and reapplying sealant or paint as needed. Regular cleaning prevents the buildup of dirt and debris, reducing the risk of deterioration. Inspect the foundation for settling and address any issues promptly.
C. Considerations for Advanced Features
Depending on the chosen plan and your skill level, you can incorporate advanced features like shelving, a work bench, or even electricity. However, ensure your electrical work adheres to all local codes and regulations. Proper grounding and wiring are essential for safety. Consult with a qualified electrician if you lack experience in electrical work.
Building a pallet shed using free plans provides a rewarding and cost-effective approach to creating valuable storage space. By meticulously following the planning and construction steps detailed above, you can construct a durable and aesthetically pleasing structure that meets your needs for years to come. Remember that safety should always be a priority; wear appropriate protective gear and follow safe working practices throughout the entire construction process.